Table Of Content

In this way the data is coded such that this column indicates the treatment given in the prior period for that cow. All ordered pairs occur an equal number of times in this design. It is balanced in terms of residual effects, or carryover effects. If we only have two treatments, we will want to balance the experiment so that half the subjects get treatment A first, and the other half get treatment B first. For example, if we had 10 subjects we might have half of them get treatment A and the other half get treatment B in the first period. After we assign the first treatment, A or B, and make our observation, we then assign our second treatment.
2 Randomized Complete Block Designs
If both of the block factors have levels that differ across the replicates, then you are in Case 3. The third case, where the replicates are different factories, can also provide a comparison of the factories. The fact that you are replicating Latin Squares does allow you to estimate some interactions that you can't estimate from a single Latin Square. If we added a treatment by factory interaction term, for instance, this would be a meaningful term in the model, and would inform the researcher whether the same protocol is best (or not) for all the factories. If the structure were a completely randomized experiment (CRD) that we discussed in lesson 3, we would assign the tips to a random piece of metal for each test. In this case, the test specimens would be considered a source of nuisance variability.
Design Systems Adoption Statistics
Once the participants are placed into blocks based on the blocking variable, we would carry out the experiment to examine the effect of cell phone use (yes vs. no) on driving ability. Those in each block will be randomly assigned into either treatment conditions of the independent variable, cell phone use (yes vs. no). As we carry out the study, participants' driving ability will be assessed. We can determine whether cell phone use has an effet on driving ability after controlling for driving experience. Latin Square Designs are probably not used as much as they should be - they are very efficient designs. In other words, these designs are used to simultaneously control (or eliminate) two sources of nuisance variability.
Analysis of BIBD's
Boston University Data Science Hub Is a Textbook Example of Jenga Architecture - Bloomberg
Boston University Data Science Hub Is a Textbook Example of Jenga Architecture.
Posted: Sat, 12 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
If both the machine and the operator have an effect on the time to produce, then by using a Latin Square Design this variation due to machine or operators will be effectively removed from the analysis. In our previous diet pills example, a blocking factor could be the sex of a patient. We could put individuals into one of two blocks (male or female).

Sums of Squares
The use of blocking in experimental design has an evolving history that spans multiple disciplines. The foundational concepts of blocking date back to the early 20th century with statisticians like Ronald A. Fisher. His work in developing analysis of variance (ANOVA) set the groundwork for grouping experimental units to control for extraneous variables. Furthermore, as mentioned early, researchers have to decide how many blocks should there be, once you have selected the blocking variable.
The following crossover design, is based on two orthogonal Latin squares. This situation can be represented as a set of 5, 2 × 2 Latin squares. Above you have the least squares means that correspond exactly to the simple means from the earlier analysis. Where F stands for “Full” and R stands for “Reduced.” The numerator and denominator degrees of freedom for the F statistic is \(df_R - df_F\) and \(df_F\) , respectively.
By randomly assigning individuals to either the new diet or the standard diet, researchers can maximize the chances that the overall level of discipline of individuals between the two groups is roughly equal. We will consider the greenhouse experiment with one factor of interest (Fertilizer). In this example, we consider Fertilizer as a fixed effect (as we are only interested in comparing the 4 fertilizers we chose for the study) and Block as a random effect. A powerful alternative to the CRD is to restrict the randomization process to form blocks. Blocks, in a physical setting such as in this example, are usually set up at right angles to suspected gradients in variation.
Table of contents
This means the effect of cell phone use treatment (yes vs. no) on the dependent variable, driving ability, should not be influenced by the level of driving experience (seasoned, intermediate, inexperienced). In other words, the impact of cell phone use treatment (yes vs. no) on the dependent variable should be similar regardless of the level of driving experience. If this assumption is violated, randomized block ANOVA should not performed.
Internet Advertising Statistics - The Rise of Mobile and Ad Blocking - Influencer Marketing Hub
Internet Advertising Statistics - The Rise of Mobile and Ad Blocking.
Posted: Tue, 30 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
In fact in this experiment the diet A consisted of only roughage, so, the cow's health might in fact deteriorate as a result of this treatment. This carryover would hurt the second treatment if the washout period isn't long enough. The measurement at this point is a direct reflection of treatment B but may also have some influence from the previous treatment, treatment A.
Again, your best bet on finding an optimal number of blocks is from theoretical and/or empirical evidences. While it is true randomized block design could be more powerful than single-factor between-subjects randomized design, this comes with an important condition. As you have seen from the procedure described above, it shouldn't come as a surprise that it is very difficult to include many blocking variables. Also, as the number of blocking variables increases, we need to create more blocks. Each block has to have a sufficient group size for statistical analysis, therefore, the sample size can increase rather quickly.
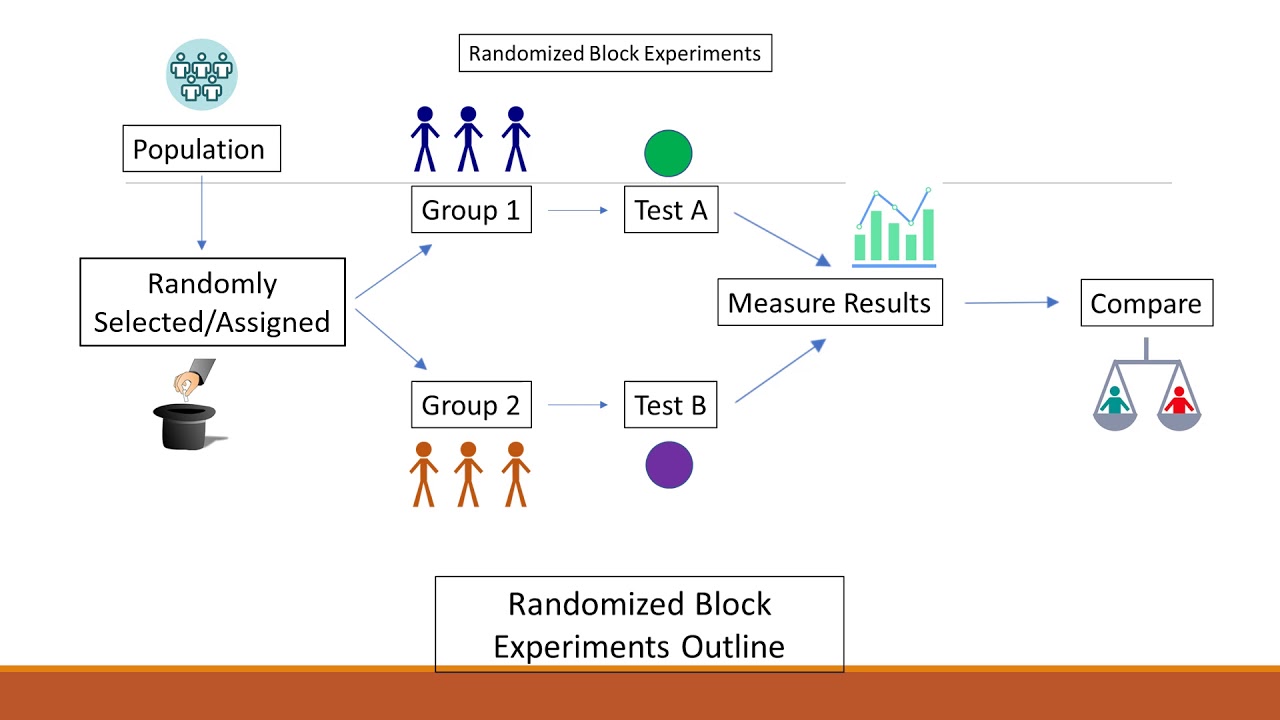
With a randomized block experiment, the main hypothesis test of interest is the test of the treatment effect(s). This kind of design is used to minimize the effects of systematic error. If the experimenter focuses exclusively on the differences between treatments, the effects due to variations between the different blocks should be eliminated. Depending on the nature of the experiment, it’s also possible to use several blocking factors at once. However, in practice only one or two are typically used since more blocking factors requires larger sample sizes to derive significant results. One common way to control for the effect of nuisance variables is through blocking, which involves splitting up individuals in an experiment based on the value of some nuisance variable.
Introduction to Statistics is our premier online video course that teaches you all of the topics covered in introductory statistics. Statology Study is the ultimate online statistics study guide that helps you study and practice all of the core concepts taught in any elementary statistics course and makes your life so much easier as a student. For example, suppose researchers want to understand the effect that a new diet has on weight less.
The plot of residuals versus order sometimes indicates a problem with the independence assumption. Here we have four blocks and within each of these blocks is a random assignment of the tips within each block. Many industrial and human subjects experiments involve blocking, or when they do not, probably should in order to reduce the unexplained variation. In the first example provided above, the sex of the patient would be a nuisance variable.

No comments:
Post a Comment